Visit the browser: Browser Address
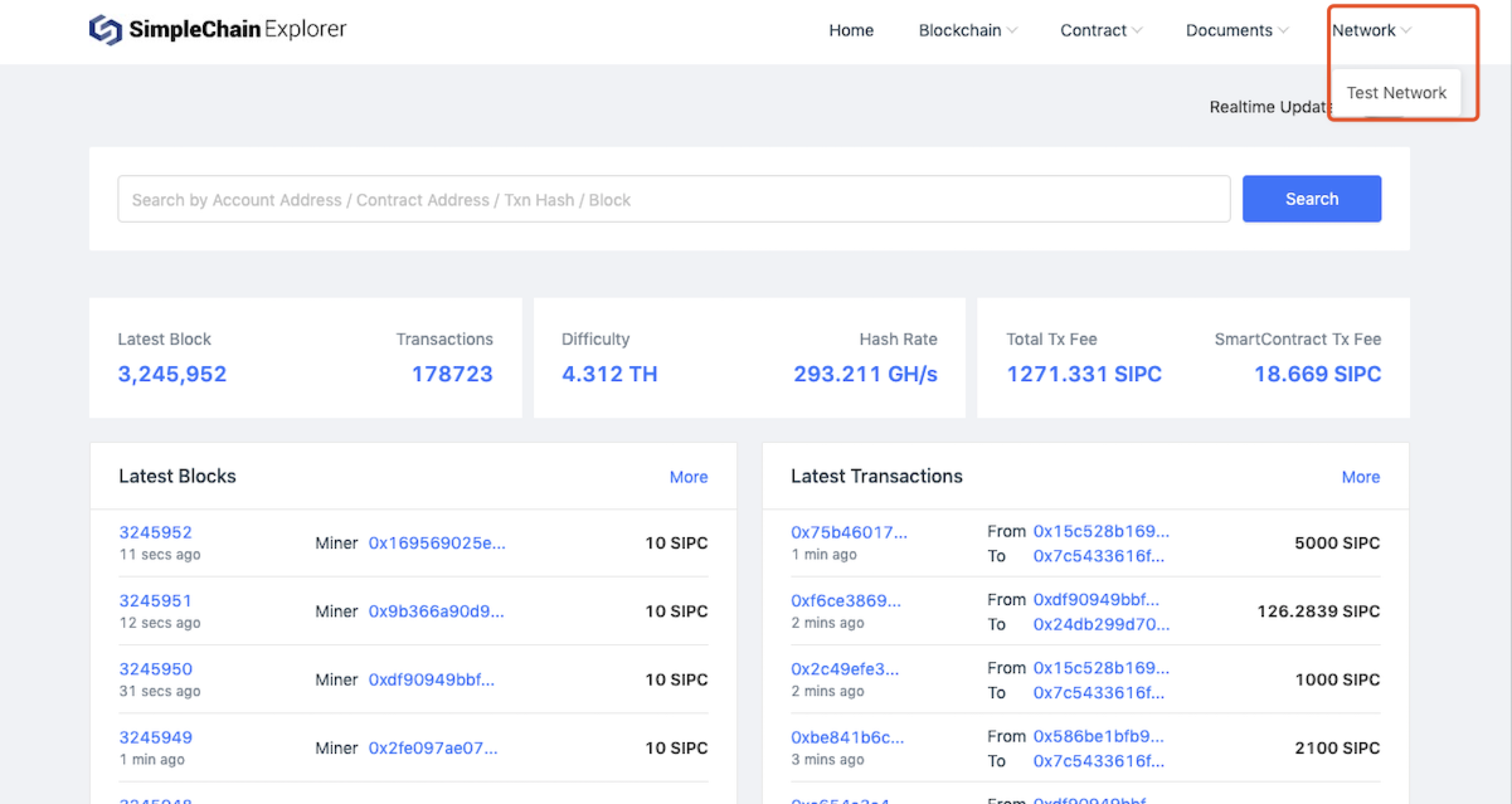
Open the Blockchain browser and switch to the Main NetWork or Test NetWork as needed. As shown below:
Block search
Information about all blocks-from Genesis blocks to all current blocks-can be found on this page, including the block height, its previous block, and the corresponding byte size.
Transaction search
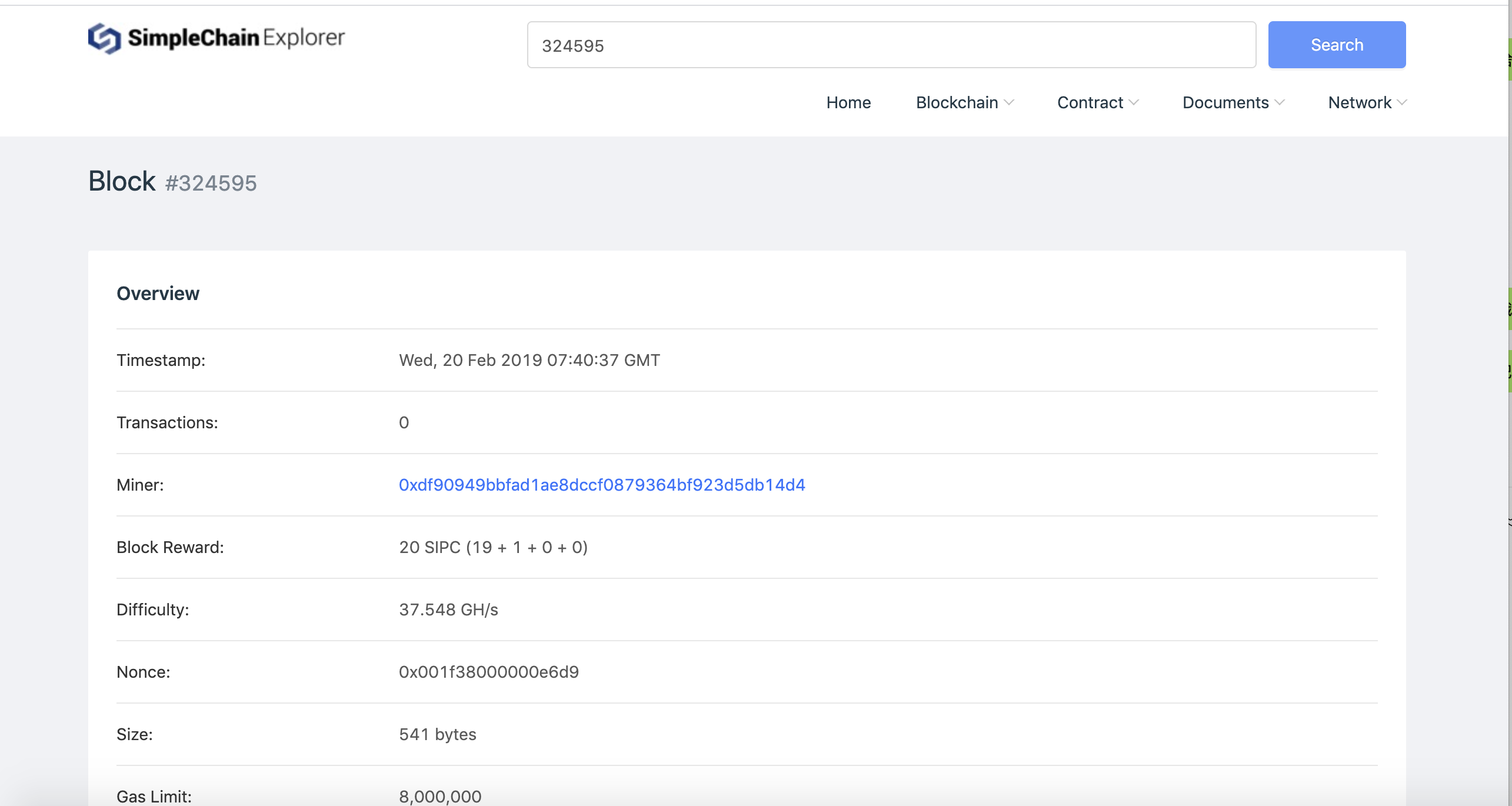
You can search for transaction records on this page. You can find the information with the sending transaction address and receiving address, the number of sipcs transmitted, the block height of the transaction record, the corresponding hash and the production time. You can also use the search bar to find specific transactions for hashes.
View uncle block
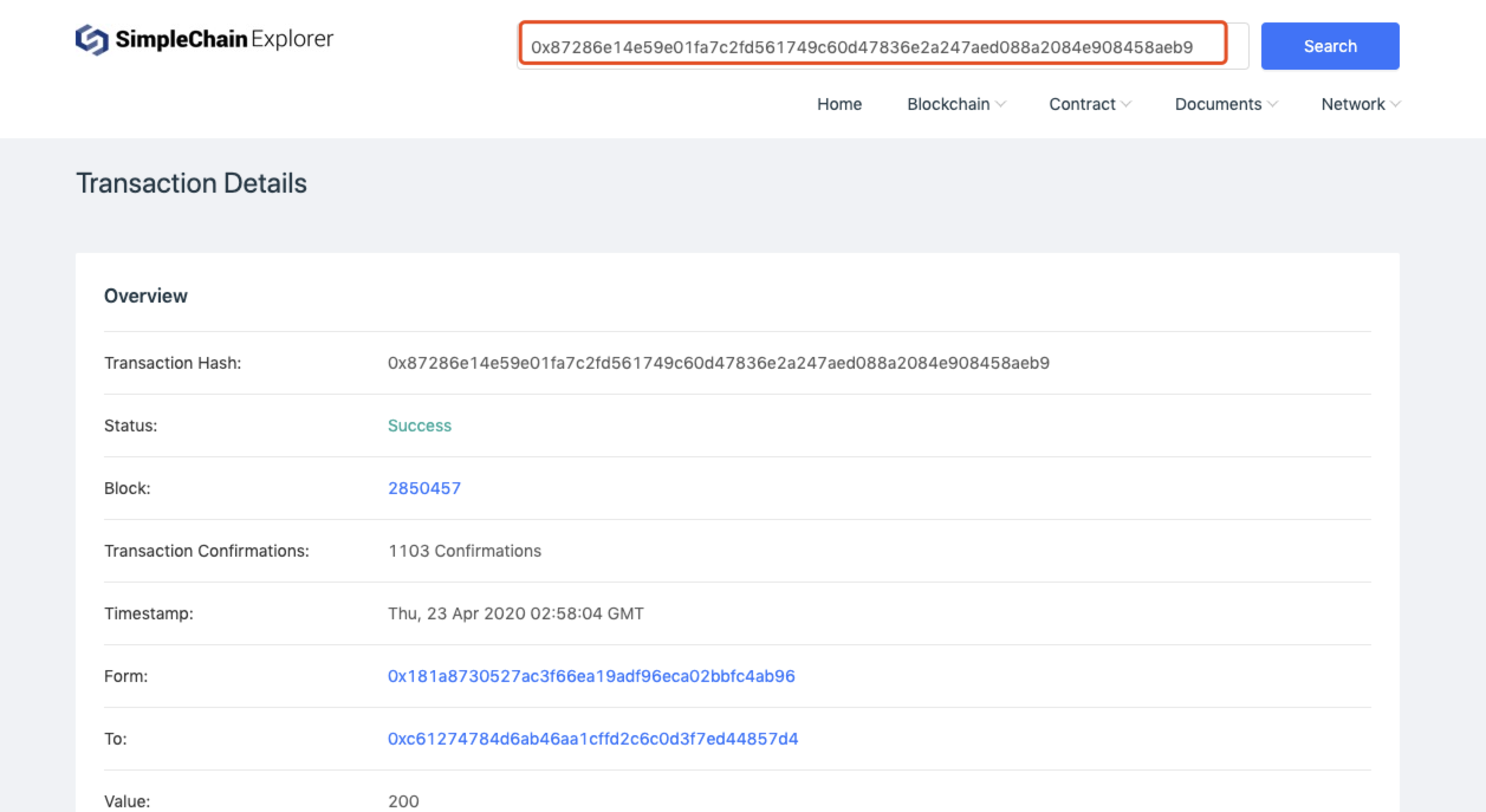
On this page, you can view the height of each block, the block height corresponding to its uncle block, the block time, and the rewards of packaged miners and miners. As shown below:
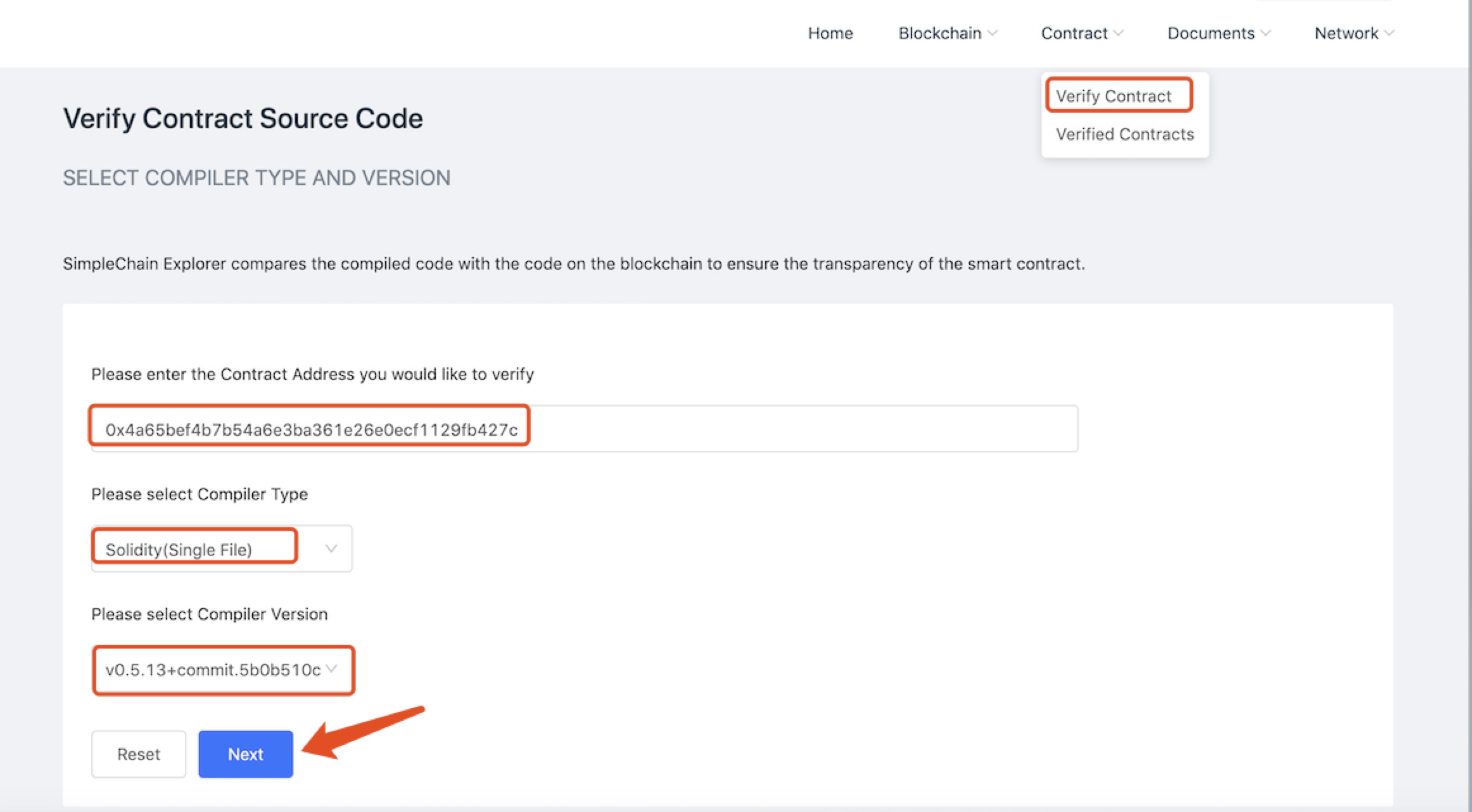
Verification contract
If you want to verify the contract, enter the contract address to be verified, and select the contract compiler type and compiler version to verify the contract. As shown below:
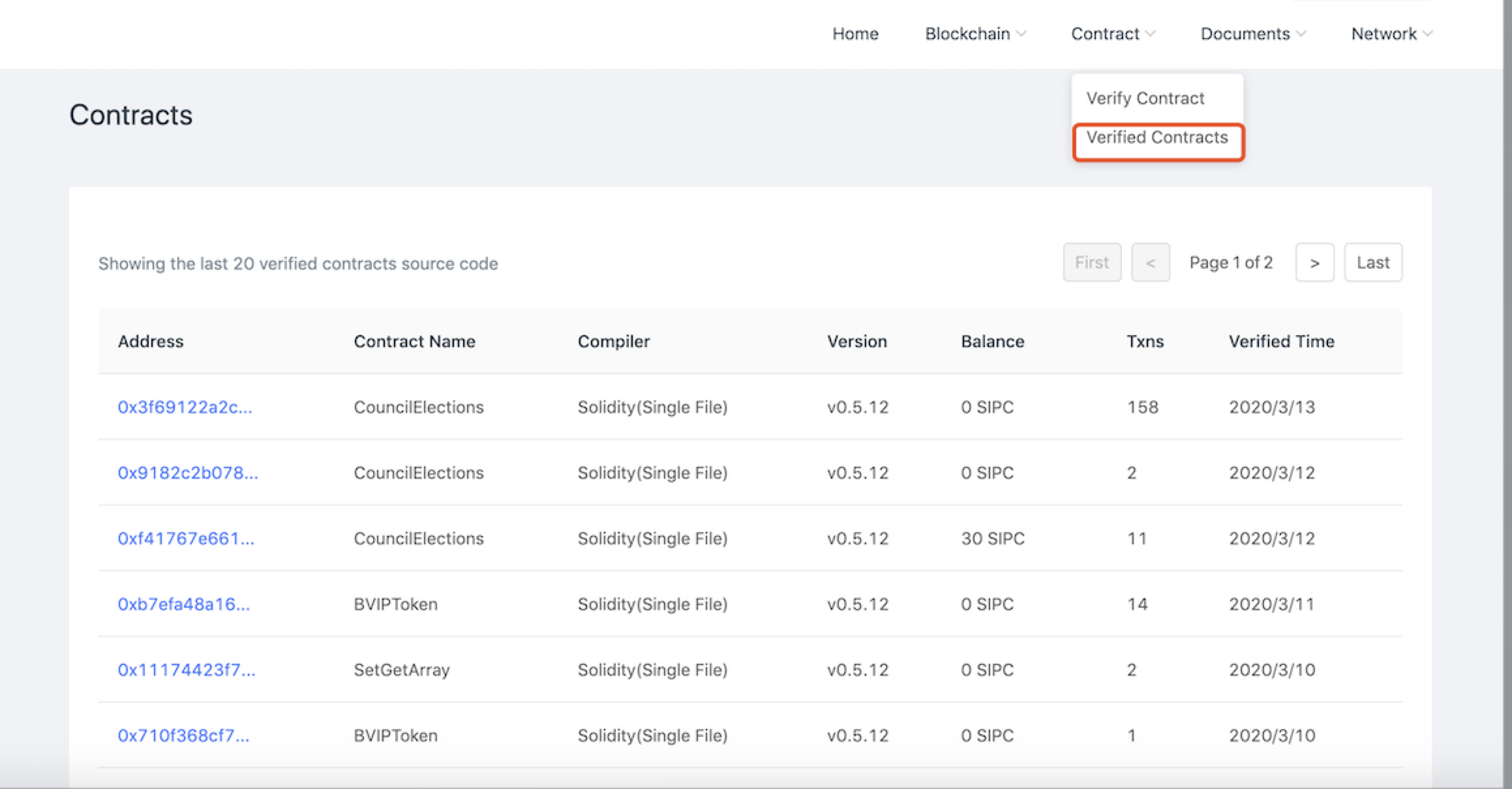
List of verified contracts
Click the verify contract list to view the information of 20 verified contracts. The information shows the contract address, contract name, compiler, version, account balance, verification time, etc!
There are three verification methods for contract verification:
- Single file verification method
- Multi-file authentication method
- Json file validation method
Single file verification
pragma solidity ^0.5.12;
contract PayALL{
event PayLog(address name,uint reward);
event PayLog2(address name);
constructor() public payable{
}
function() external payable{
emit PayLog(msg.sender, msg.value);
}
function setMethd() public payable {
emit PayLog2(msg.sender);
}
}

Paste source code:

After the verification is passed:

Multi-file verification
Because in the contract writing process, the dependency of the file can refer to another file.
// test1.sol文件
pragma solidity ^0.5.17;
contract Hello {
uint value;
function hello() public pure returns(string memory){
return "hello world_1";
}
function set(uint x) public {
value = x;
}
}
// test2.sol文件
pragma solidity ^0.5.17;
import {Hello} from "./test1.sol" ;
contract Test2 is Hello {
function test() public pure returns(string memory){
return Hello.hello();
}
}

Execution result:

This type of authentication is used for multi-file authentication. The verification method is as follows to obtain the deployed contract address:
0x6e1ace6e6cf09a4ab096f272cfc029c0a1d883ac


Optimizationit refers to the number of contract compilation times. The number of optimized times is selected for contract deployment. Therefore, the corresponding number of times must be selected for verification. By default, no optimization is performed.
Constructor Arguments ABI-encoded indicates whether the contract has construction parameters. The construction parameters are generated during deployment. You do not need to fill in the construction parameters for verification.
Contract Library Address When it comes to library contracts, ordinary contracts are not filled in. Details of this type of verification will be added later.
View verification successful

Multi-file contract source code after current verification

The source code is displayed in json format, including two file source codes.
Json file validation:
The Json file verification method is relatively copied. You need to know the compilation parameters of solidity. solidity compiles the json file passed by the user, provided that the json file meets the compilation requirements.
Json file:
{
"language": "Solidity",
"sources": {
"myFile.sol": {
"content": "pragma solidity ^0.5.12;contract Multiply7 { event Print(uint); event CjLog(address, uint); uint public a ; uint public b ; constructor (uint _a, uint _b) public { a = _a; b = _b; } function multiply(uint input1) public view returns (uint) { return input1 * 6 + a + b; } function multiplyplus(uint input1, uint input2) public returns (uint) { emit Print(input1 * 6 * input2); emit CjLog(msg.sender, a+b); return input1 * 6 * input2 + a + b; }}"
}
},
"settings": {
"metadata": {
"useLiteralContent": true
},
"outputSelection": {
"*": {
"*": [
"*"
],
"": [
"ast"
]
}
}
}
}


Library contract verification
First of all, understand what is a library contract
Browser support library the contract verification of the library,Library during the deployment process, contracts are deployed in sequence and nested. All contracts are deployed with multiple contracts (including library libraries inside the contracts, which are deployed together) and multiple hash records are generated.
Contract source code:
/**
*Submitted for verification at Etherscan.io on 2020-02-27
*/
pragma solidity ^0.6.0;
library SetHFG {
// 我们定义了一个新的结构体数据类型,用于在调用合约中保存数据。
struct Data { mapping(uint => bool) flags; }
// 注意第一个参数是“storage reference”类型,因此在调用中参数传递的只是它的存储地址而不是内容。
// 这是库函数的一个特性。如果该函数可以被视为对象的方法,则习惯称第一个参数为 `self` 。
function insert(Data storage self, uint value)
public
returns (bool)
{
if (self.flags[value])
return false; // 已经存在
self.flags[value] = true;
Acc.hi();
return true;
}
the following is the deployment record:

CHU as the main contract: 0x1c622ed2035acc8514259788caafb3cf69d9bbe3
The contract address of the Library is:
Bcc:0x0da8bd0dd96f78ac6e155b2d5e9fb6d15ca89fad
Fcc:0x7b05897e605a3878d3511069924d750ef3954da5
Acc:0x13a6cb372333394caa8ea0e5876a4a52167a95ce
SetHFG: 0x5386710eb4d02b41e7a253d3ebb00ca8795c930f
Verification way and single-file same, as shown below:


Verification passed

